Vaginal surgery is a discipline in itself. A number of procedures can be performed by the vaginal route. Vaginal surgery is most commonly performed when the uterus has to be removed or its position has to be corrected.
The uterus may have to be removed when women have symptoms due to fibroids or when there is excessive vaginal bleeding. The uterus may be enlarged in these situations. But in most circumstances, it is still possible to remove the uterus from the vaginal route with specific skills. The advantages of a vaginal hysterectomy to the woman are numerous. There is no scar on her body and she does not have to worry about dressings or stitches being removed. The pain after surgery and the need to rest is much lesser as compared to a hysterectomy done by opening the abdomen or through a laparoscope. The woman is on her feet and back to her routine much faster after a vaginal hysterectomy.
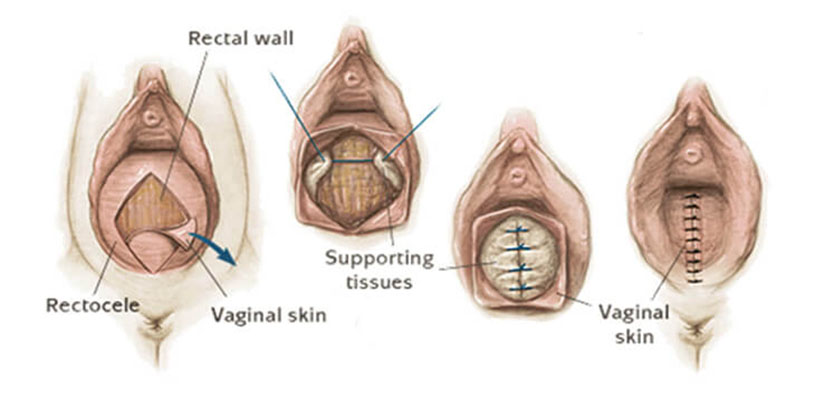
The position of the uterus and the surrounding organs may descend in a condition called genital prolapse. This results from a weakening of the normal supports of the pelvic organs and can affect the position of the bladder, uterus, intestines, and rectum. Surgical correction can be done by the vaginal route. If the woman so desires, the uterus can be conserved. Usually, this condition affects older women who have completed their families. In such situations, the removal of the uterus and repair of the weakened supports can be achieved. Cysts of the ovaries which are known to not be cancer can also be treated by vaginal surgery.